CMI, dosage, igredients, description, price, photo
What is lorazepam?
Lorazepam belongs to a group of drugs called benzodiazepines. It affects chemicals in the brain that may be unbalanced in people with anxiety.
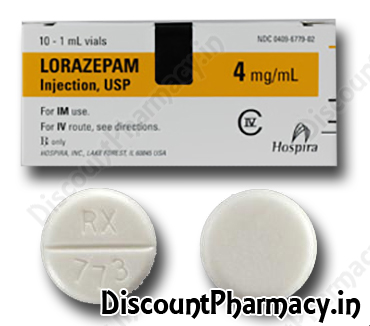
lorazepam
Lorazepam is used to treat anxiety disorders.
Lorazepam may also be used for purposes not listed in this medication guide.
Important information
You should not use lorazepam if you have narrow-angle glaucoma or myasthenia gravis, or if you are allergic to Valium or a similar medicine.
Do not use lorazepam if you are pregnant. This medicine can cause birth defects or life-threatening withdrawal symptoms in a newborn.
Lorazepam may be habit-forming and should be used only by the person it was prescribed for. Misuse of habit-forming medicine can cause addiction, overdose, or death. Lorazepam should never be shared with another person, especially someone who has a history of drug abuse or addiction. Keep the medication in a secure place where others cannot get to it.
Do not drink alcohol while taking lorazepam. This medication can increase the effects of alcohol.
Before taking this medicine
It is dangerous to purchase lorazepam on the Internet or from vendors outside the United States. Medications distributed from Internet sales may contain dangerous ingredients, or may not be distributed by a licensed pharmacy. The sale and distribution of lorazepam outside the U.S. does not comply with the regulations of the Food and Drug Administration (FDA) for the safe use of this medication.
You should not take lorazepam if you have:
- narrow-angle glaucoma;
- myasthenia gravis; or
- a history of allergic reaction to any benzodiazepine, such as diazepam (Valium), chlordiazepoxide, clonazepam, flurazepam, and others.
To make sure lorazepam is safe for you, tell your doctor if you have:
- seizures or epilepsy;
- kidney or liver disease (especially alcoholic liver disease);
- asthma or other breathing disorder;
- open-angle glaucoma;
- a history of depression or suicidal thoughts or behavior; or
- a history of drug or alcohol addiction.
Do not use lorazepam if you are pregnant. This medicine can cause birth defects. Your baby could also become dependent on the drug. This can cause life-threatening withdrawal symptoms in the baby after it is born. Babies born dependent on habit-forming medicine may need medical treatment for several weeks. Tell your doctor if you are pregnant or plan to become pregnant. Use effective birth control to prevent pregnancy while you are taking lorazepam.
Lorazepam can pass into breast milk and may harm a nursing baby. You should not breast-feed while you are using this medicine.
Lorazepam is not approved for use by anyone younger than 18 years old.
The sedative effects of lorazepam may last longer in older adults. Accidental falls are common in elderly patients who take benzodiazepines. Use caution to avoid falling or accidental injury while you are taking lorazepam.
How should I take lorazepam?
Take lorazepam exactly as it was prescribed for you. Follow all directions on your prescription label. Never use this medicine in larger amounts, or for longer than prescribed. Tell your doctor if the medicine seems to stop working as well in treating your symptoms.
Lorazepam may be habit-forming. Never share this medicine with another person, especially someone with a history of drug abuse or addiction. Keep the medication in a place where others cannot get to it.
Misuse of habit-forming medicine can cause addiction, overdose, or death. Selling or giving away this medicine is against the law.
Measure liquid medicine with the dosing syringe provided, or with a special dose-measuring spoon or medicine cup. If you do not have a dose-measuring device, ask your pharmacist for one.
Lorazepam should be used for only a short time. Do not take this medicine for longer than your doctor recommends.
Do not stop using lorazepam suddenly or you could have unpleasant withdrawal symptoms, including a seizure (convulsions). Ask your doctor how to safely stop using this medicine.
Call your doctor if this medicine seems to stop working as well in treating your anxiety symptoms.
Keep track of the amount of medicine used from each new bottle. Lorazepam is a drug of abuse and you should be aware if anyone is using your medicine improperly or without a prescription.
Store lorazepam tablets at room temperature away from moisture, heat, and light. Store the liquid form of this medicine in the refrigerator.
What happens if I miss a dose?
Take the missed dose as soon as you remember. Skip the missed dose if it is almost time for your next scheduled dose. Do not take extra medicine to make up the missed dose.
What happens if I overdose?
Seek emergency medical attention or call the Poison Help line at 1-800-222-1222. An overdose of lorazepam can be fatal. Overdose symptoms may include extreme drowsiness, confusion, muscle weakness, loss of balance or coordination, feeling light-headed, and fainting.
What should I avoid while taking lorazepam?
Do not drink alcohol while taking lorazepam. This medication can increase the effects of alcohol.
Lorazepam may impair your thinking or reactions. Avoid driving or operating machinery until you know how this medicine will affect you. Dizziness or severe drowsiness can cause falls or other accidents.
Lorazepam side effects
Get emergency medical help if you have signs of an allergic reaction to lorazepam: hives; difficulty breathing; swelling of your face, lips, tongue, or throat.
Call your doctor at once if you have:
- severe drowsiness;
- thoughts of suicide or hurting yourself;
- unusual changes in mood or behavior;
- confusion, aggression, hallucinations;
- worsened sleep problems;
- sudden restless feeling or excitement;
- muscle weakness, drooping eyelids, trouble swallowing;
- vision changes; or
- upper stomach pain, dark urine, jaundice (yellowing of the skin or eyes).
Common lorazepam side effects may include:
- dizziness, drowsiness;
- weakness;
- slurred speech, lack of balance or coordination;
- memory problems; or
- feeling unsteady.
This is not a complete list of side effects and others may occur. Tell your doctor about any unusual or bothersome side effect.
Lorazepam dosing information
Usual Adult Dose of Lorazepam for Anxiety:
Tablets:
Initial dose: 2 to 3 mg orally per day administered 2 to 3 times per day
Maintenance dose: 1 to 2 mg orally 2 to 3 times a day
Parenteral:
IV: 2 mg total, or 0.044 mg/kg, whichever is smaller
Comments:
-The daily dosage may vary from 1 to 10 mg per day.
-The dosage should be increased gradually when needed to help avoid adverse effects.
-When higher dosage is indicated, the evening dose should be increased before the daytime doses.
Use: Management of anxiety disorders or for the short-term relief of the symptoms of anxiety or anxiety associated with depressive symptoms
Usual Adult Dose for Light Anesthesia:
IM: 0.05 mg/kg up to a maximum of 4 mg
IV: 2 mg total, or 0.044 mg/kg, whichever is smaller
Comments:
-Doses of other injectable central-nervous-system depressant drugs should be reduced.
-For optimum effect, intramuscular drug should be administered at least 2 hours before the anticipated operative procedure.
-Narcotic analgesics should be administered at their usual preoperative time.
-IV: This dose should not ordinarily be exceeded in patients over 50 years of age.
-IV: Larger doses as high as 0.05 mg/kg up to a total of 4 mg may be administered.
-For optimum effect, intravenous drug should be administered 15 to 20 minutes before the anticipated operative procedure.
Use:
-Preanesthetic medication for adult patients, producing sedation (sleepiness or drowsiness), relief of anxiety, and a decreased ability to recall events related to the day of surgery
Usual Adult Dose for Status Epilepticus:
0.1 mg/kg IV up to 4 mg per dose; may repeat in 5 to 10 minutes
Maximum dose: 8 mg
Comments:
-Vital signs should be monitored, an unobstructed airway should be maintained, and artificial ventilation equipment should be available.
-When an intravenous port is not available, the IM route may prove useful.
Use: Treatment of status epilepticus
Usual Adult Dose for Insomnia:
2 to 4 mg orally administered at bedtime
Comments:
-The dosage should be increased gradually when needed to help avoid adverse effects.
Use: Management of insomnia
Usual Geriatric Dose for Anxiety:
Elderly or debilitated patients:
1 to 2 mg orally per day in divided doses
Comments:
-The dosage should be increased gradually when needed to help avoid adverse effects.
Use: Management of anxiety disorders or for the short-term relief of the symptoms of anxiety or anxiety associated with depressive symptoms
Usual Pediatric Dose for Anxiety:
12 years or older:
Initial dose: 2 to 3 mg orally per day administered 2 to 3 times per day
Maintenance dose: 1 to 2 mg orally 2 to 3 times a day
Comments:
-The daily dosage may vary from 1 to 10 mg per day.
-The dosage should be increased gradually when needed to help avoid adverse effects.
-When higher dosage is indicated, the evening dose should be increased before the daytime doses.
Use: Management of anxiety disorders or for the short-term relief of the symptoms of anxiety or anxiety associated with depressive symptoms
Usual Pediatric Dose for Insomnia:
12 years or older:
2 to 4 mg orally administered at bedtime
Comments:
-For elderly or debilitated patients, an initial dosage of 1 to 2 mg/day in divided doses is recommended.
-The dosage should be increased gradually when needed to help avoid adverse effects.
Use: Management of insomnia
What other drugs will affect lorazepam?
Taking this medicine with other drugs that make you sleepy or slow your breathing can cause dangerous or life-threatening side effects. Ask your doctor before taking lorazepam with a sleeping pill, narcotic pain medicine, muscle relaxer, or medicine for depression or seizures.
Tell your doctor about all your current medicines and any you start or stop using, especially:
- any other medicines to treat anxiety;
- probenecid;
- aminophylline or theophylline;
- an antidepressant, or medicine to treat mental illness;
- a barbiturate such as phenobarbital;
- narcotic pain medicine;
- seizure medicine; or
- medicine that contains an antihistamine (such as sleep medicine, cold or allergy medicine).
This list is not complete. Other drugs may interact with lorazepam, including prescription and over-the-counter medicines, vitamins, and herbal products. Not all possible interactions are listed in this medication guide.